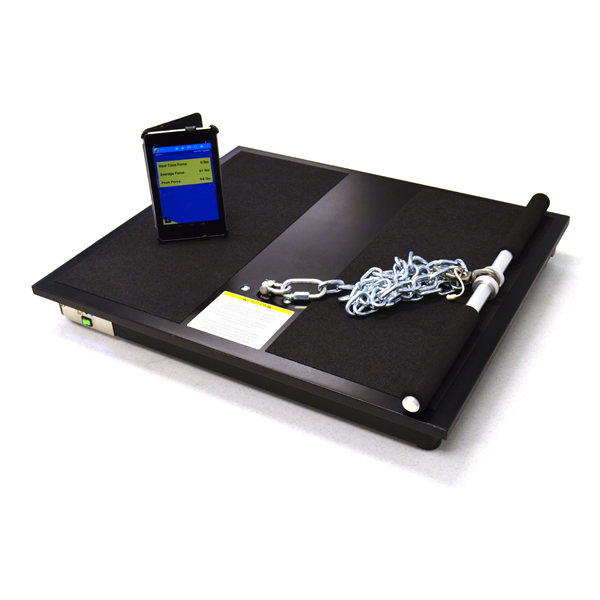
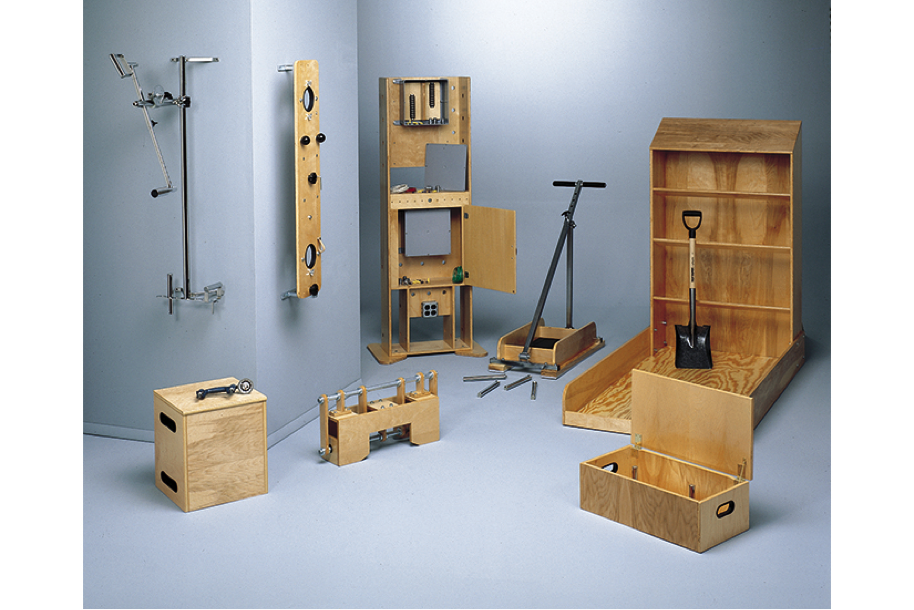
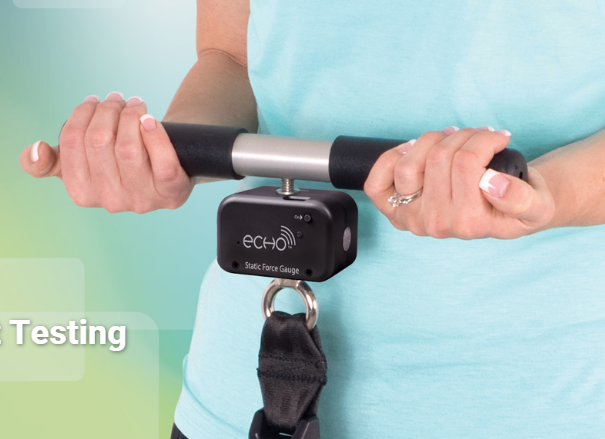
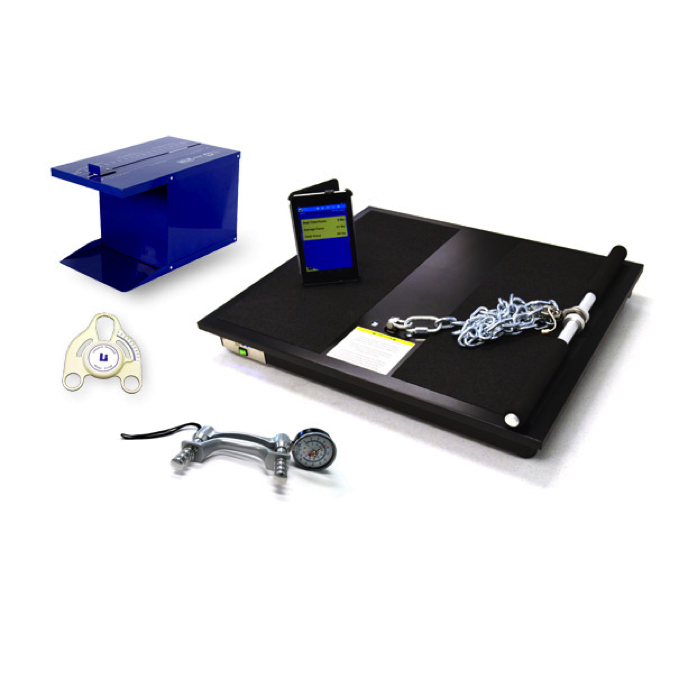
PHYSICAL WORK CAPACITY AND FUNCTIONAL CAPACITY EVALUATION SYSTEM Model 32601PWCFC DETAILS The two components of the PWCFC Evaluation System are Physical Work Capacity (PWC) and Functional Capacity (FC). The Physical Work Capacity component evaluates the capacity of an individual to perform physically demanding work tasks. System input includes the physical ability test results and demographic data. Output is a computergenerated report that assesses the Physical Work Capacity. The report helps employers make either of two employment decisions, which are: Pre-employment: The PWC report evaluates the capacity of a job applicant to perform physically demanding work tasks. Return-to-Work: The FC report evaluates the capacity of an employee to perform physically demanding tasks at a level that allows for the safe return to work. Data used to develop the Physical Work Capacity evaluation comes from 20 years of preemployment research completed at the University of Houston. The purpose of this research was to validate pre-employment tests and define physiologically justified standards or accurate scores. The ergonomic principle is to match the worker to the demands of the job. This validation research is the linkage between test results and job tasks. The Functional Capacity component assesses Work Capacity and physical fitness. The fitness components include maximum aerobic capacity (VO2max), body composition, and flexibility. These are the common components included in adult fitness test batteries (Baumgartner & Jackson, 1999; Golding, Meyers & Sinning, 1989).
PHYSICAL WORK CAPACITY AND FUNCTIONAL CAPACITY EVALUATION SYSTEM Model 32601PWCFC DETAILS The two components of the PWCFC Evaluation System are Physical Work Capacity (PWC) and Functional Capacity (FC). The Physical Work Capacity component evaluates the capacity of an individual to perform physically demanding work tasks. System input includes the physical ability test results and demographic data. Output is a computergenerated report that assesses the Physical Work Capacity. The report helps employers make either of two employment decisions, which are: Pre-employment: The PWC report evaluates the capacity of a job applicant to perform physically demanding work tasks. Return-to-Work: The FC report evaluates the capacity of an employee to perform physically demanding tasks at a level that allows for the safe return to work. Data used to develop the Physical Work Capacity evaluation comes from 20 years of preemployment research completed at the University of Houston. The purpose of this research was to validate pre-employment tests and define physiologically justified standards or accurate scores. The ergonomic principle is to match the worker to the demands of the job. This validation research is the linkage between test results and job tasks. The Functional Capacity component assesses Work Capacity and physical fitness. The fitness components include maximum aerobic capacity (VO2max), body composition, and flexibility. These are the common components included in adult fitness test batteries (Baumgartner & Jackson, 1999; Golding, Meyers & Sinning, 1989).

32601PWCFC型体能及功能性能力评估系统
32601PWCFC型体能及功能性能力评估系统(PHYSICAL WORK CAPACITY AND FUNCTIONAL CAPACITY EVALUATION SYSTEM, Model 32601PWCFC),该系统主要用于职业康复评估——体力劳动能力评估(Physical Work Capacity,PWC),以及职业康复评估——功能性能力评估(Functional Capacity Evaluation, FCE)。配置有计算机软件系统,输入包括体能测试结果和个人数据,系统通过软件自动分析测试结果,将自动生成实际工作能力的评估报告。32601PWCFC型体能及功能性能力评估系统,是入职前,评估求职者执行体力劳动任务的能力,以及返回工作岗位前,评估员工是否被允许重返工作岗位执行体力劳动任务的能力和安全性。
32601PWCFC型体能及功能性能力评估系统,用于开展体力劳动能力评估的数据来自休斯顿大学近20年的研究。这项研究的目的是验证就业前的测试,并确定生理上合理的标准或准确的分数,并且符合人体工程学的原则,使工人与工作的要求相匹配。该验证研究结果是评估测试和工作任务之间的桥梁。
功能性能力评估部分,主要评估身体柔韧性和身体成分,以及有氧工作能力等方面。使用Baseline®坐位体前屈躯干柔韧性测试仪和Lafayette®大测距皮褶厚度计等工具完成相应的测试工作。(Baumgartner & Jackson, 1999; Golding, Meyers & Sinning, 1989).
原装进口
| 32601PWCFC | 32601PWCFC型体能及功能性能力评估系统 | 电邮询价 |
PHYSICAL WORK CAPACITY AND FUNCTIONAL CAPACITY EVALUATION SYSTEM Model 32601PWCFC DETAILS The two components of the PWCFC Evaluation System are Physical Work Capacity (PWC) and Functional Capacity (FC). The Physical Work Capacity component evaluates the capacity of an individual to perform physically demanding work tasks. System input includes the physical ability test results and demographic data. Output is a computergenerated report that assesses the Physical Work Capacity. The report helps employers make either of two employment decisions, which are: Pre-employment: The PWC report evaluates the capacity of a job applicant to perform physically demanding work tasks. Return-to-Work: The FC report evaluates the capacity of an employee to perform physically demanding tasks at a level that allows for the safe return to work. Data used to develop the Physical Work Capacity evaluation comes from 20 years of preemployment research completed at the University of Houston. The purpose of this research was to validate pre-employment tests and define physiologically justified standards or accurate scores. The ergonomic principle is to match the worker to the demands of the job. This validation research is the linkage between test results and job tasks. The Functional Capacity component assesses Work Capacity and physical fitness. The fitness components include maximum aerobic capacity (VO2max), body composition, and flexibility. These are the common components included in adult fitness test batteries (Baumgartner & Jackson, 1999; Golding, Meyers & Sinning, 1989).
PHYSICAL WORK CAPACITY AND FUNCTIONAL CAPACITY EVALUATION SYSTEM Model 32601PWCFC DETAILS The two components of the PWCFC Evaluation System are Physical Work Capacity (PWC) and Functional Capacity (FC). The Physical Work Capacity component evaluates the capacity of an individual to perform physically demanding work tasks. System input includes the physical ability test results and demographic data. Output is a computergenerated report that assesses the Physical Work Capacity. The report helps employers make either of two employment decisions, which are: Pre-employment: The PWC report evaluates the capacity of a job applicant to perform physically demanding work tasks. Return-to-Work: The FC report evaluates the capacity of an employee to perform physically demanding tasks at a level that allows for the safe return to work. Data used to develop the Physical Work Capacity evaluation comes from 20 years of preemployment research completed at the University of Houston. The purpose of this research was to validate pre-employment tests and define physiologically justified standards or accurate scores. The ergonomic principle is to match the worker to the demands of the job. This validation research is the linkage between test results and job tasks. The Functional Capacity component assesses Work Capacity and physical fitness. The fitness components include maximum aerobic capacity (VO2max), body composition, and flexibility. These are the common components included in adult fitness test batteries (Baumgartner & Jackson, 1999; Golding, Meyers & Sinning, 1989).
PHYSICAL WORK CAPACITY AND FUNCTIONAL CAPACITY EVALUATION SYSTEM, Model 32601PWCFC DETAILS The two components of the PWCFC Evaluation System are Physical Work Capacity (PWC) and Functional Capacity (FC). The Physical Work Capacity component evaluates the capacity of an individual to perform physically demanding work tasks. System input includes the physical ability test results and demographic data. Output is a computergenerated report that assesses the Physical Work Capacity. The report helps employers make either of two employment decisions, which are: Pre-employment: The PWC report evaluates the capacity of a job applicant to perform physically demanding work tasks. Return-to-Work: The FC report evaluates the capacity of an employee to perform physically demanding tasks at a level that allows for the safe return to work. Data used to develop the Physical Work Capacity evaluation comes from 20 years of preemployment research completed at the University of Houston. The purpose of this research was to validate pre-employment tests and define physiologically justified standards or accurate scores. The ergonomic principle is to match the worker to the demands of the job. This validation research is the linkage between test results and job tasks. The Functional Capacity component assesses Work Capacity and physical fitness. The fitness components include maximum aerobic capacity (VO2max), body composition, and flexibility. These are the common components included in adult fitness test batteries (Baumgartner & Jackson, 1999; Golding, Meyers & Sinning, 1989).
PHYSICAL WORK CAPACITY AND FUNCTIONAL CAPACITY EVALUATION SYSTEM, Model 32601PWCFC DETAILS The two components of the PWCFC Evaluation System are Physical Work Capacity (PWC) and Functional Capacity (FC). The Physical Work Capacity component evaluates the capacity of an individual to perform physically demanding work tasks. System input includes the physical ability test results and demographic data. Output is a computergenerated report that assesses the Physical Work Capacity. The report helps employers make either of two employment decisions, which are: Pre-employment: The PWC report evaluates the capacity of a job applicant to perform physically demanding work tasks. Return-to-Work: The FC report evaluates the capacity of an employee to perform physically demanding tasks at a level that allows for the safe return to work. Data used to develop the Physical Work Capacity evaluation comes from 20 years of preemployment research completed at the University of Houston. The purpose of this research was to validate pre-employment tests and define physiologically justified standards or accurate scores. The ergonomic principle is to match the worker to the demands of the job. This validation research is the linkage between test results and job tasks. The Functional Capacity component assesses Work Capacity and physical fitness. The fitness components include maximum aerobic capacity (VO2max), body composition, and flexibility. These are the common components included in adult fitness test batteries (Baumgartner & Jackson, 1999; Golding, Meyers & Sinning, 1989).
PHYSICAL WORK CAPACITY AND FUNCTIONAL CAPACITY EVALUATION SYSTEM, Model 32601PWCFC DETAILS The two components of the PWCFC Evaluation System are Physical Work Capacity (PWC) and Functional Capacity (FC). The Physical Work Capacity component evaluates the capacity of an individual to perform physically demanding work tasks. System input includes the physical ability test results and demographic data. Output is a computergenerated report that assesses the Physical Work Capacity. The report helps employers make either of two employment decisions, which are: Pre-employment: The PWC report evaluates the capacity of a job applicant to perform physically demanding work tasks. Return-to-Work: The FC report evaluates the capacity of an employee to perform physically demanding tasks at a level that allows for the safe return to work. Data used to develop the Physical Work Capacity evaluation comes from 20 years of preemployment research completed at the University of Houston. The purpose of this research was to validate pre-employment tests and define physiologically justified standards or accurate scores. The ergonomic principle is to match the worker to the demands of the job. This validation research is the linkage between test results and job tasks. The Functional Capacity component assesses Work Capacity and physical fitness. The fitness components include maximum aerobic capacity (VO2max), body composition, and flexibility. These are the common components included in adult fitness test batteries (Baumgartner & Jackson, 1999; Golding, Meyers & Sinning, 1989).
PHYSICAL WORK CAPACITY AND FUNCTIONAL CAPACITY EVALUATION SYSTEM, Model 32601PWCFC DETAILS The two components of the PWCFC Evaluation System are Physical Work Capacity (PWC) and Functional Capacity (FC). The Physical Work Capacity component evaluates the capacity of an individual to perform physically demanding work tasks. System input includes the physical ability test results and demographic data. Output is a computergenerated report that assesses the Physical Work Capacity. The report helps employers make either of two employment decisions, which are: Pre-employment: The PWC report evaluates the capacity of a job applicant to perform physically demanding work tasks. Return-to-Work: The FC report evaluates the capacity of an employee to perform physically demanding tasks at a level that allows for the safe return to work. Data used to develop the Physical Work Capacity evaluation comes from 20 years of preemployment research completed at the University of Houston. The purpose of this research was to validate pre-employment tests and define physiologically justified standards or accurate scores. The ergonomic principle is to match the worker to the demands of the job. This validation research is the linkage between test results and job tasks. The Functional Capacity component assesses Work Capacity and physical fitness. The fitness components include maximum aerobic capacity (VO2max), body composition, and flexibility. These are the common components included in adult fitness test batteries (Baumgartner & Jackson, 1999; Golding, Meyers & Sinning, 1989).
PHYSICAL WORK CAPACITY AND FUNCTIONAL CAPACITY EVALUATION SYSTEM, Model 32601PWCFC DETAILS The two components of the PWCFC Evaluation System are Physical Work Capacity (PWC) and Functional Capacity (FC). The Physical Work Capacity component evaluates the capacity of an individual to perform physically demanding work tasks. System input includes the physical ability test results and demographic data. Output is a computergenerated report that assesses the Physical Work Capacity. The report helps employers make either of two employment decisions, which are: Pre-employment: The PWC report evaluates the capacity of a job applicant to perform physically demanding work tasks. Return-to-Work: The FC report evaluates the capacity of an employee to perform physically demanding tasks at a level that allows for the safe return to work. Data used to develop the Physical Work Capacity evaluation comes from 20 years of preemployment research completed at the University of Houston. The purpose of this research was to validate pre-employment tests and define physiologically justified standards or accurate scores. The ergonomic principle is to match the worker to the demands of the job. This validation research is the linkage between test results and job tasks. The Functional Capacity component assesses Work Capacity and physical fitness. The fitness components include maximum aerobic capacity (VO2max), body composition, and flexibility. These are the common components included in adult fitness test batteries (Baumgartner & Jackson, 1999; Golding, Meyers & Sinning, 1989).
PHYSICAL WORK CAPACITY AND FUNCTIONAL CAPACITY EVALUATION SYSTEM, Model 32601PWCFC DETAILS The two components of the PWCFC Evaluation System are Physical Work Capacity (PWC) and Functional Capacity (FC). The Physical Work Capacity component evaluates the capacity of an individual to perform physically demanding work tasks. System input includes the physical ability test results and demographic data. Output is a computergenerated report that assesses the Physical Work Capacity. The report helps employers make either of two employment decisions, which are: Pre-employment: The PWC report evaluates the capacity of a job applicant to perform physically demanding work tasks. Return-to-Work: The FC report evaluates the capacity of an employee to perform physically demanding tasks at a level that allows for the safe return to work. Data used to develop the Physical Work Capacity evaluation comes from 20 years of preemployment research completed at the University of Houston. The purpose of this research was to validate pre-employment tests and define physiologically justified standards or accurate scores. The ergonomic principle is to match the worker to the demands of the job. This validation research is the linkage between test results and job tasks. The Functional Capacity component assesses Work Capacity and physical fitness. The fitness components include maximum aerobic capacity (VO2max), body composition, and flexibility. These are the common components included in adult fitness test batteries (Baumgartner & Jackson, 1999; Golding, Meyers & Sinning, 1989).
PHYSICAL WORK CAPACITY AND FUNCTIONAL CAPACITY EVALUATION SYSTEM, Model 32601PWCFC DETAILS The two components of the PWCFC Evaluation System are Physical Work Capacity (PWC) and Functional Capacity (FC). The Physical Work Capacity component evaluates the capacity of an individual to perform physically demanding work tasks. System input includes the physical ability test results and demographic data. Output is a computergenerated report that assesses the Physical Work Capacity. The report helps employers make either of two employment decisions, which are: Pre-employment: The PWC report evaluates the capacity of a job applicant to perform physically demanding work tasks. Return-to-Work: The FC report evaluates the capacity of an employee to perform physically demanding tasks at a level that allows for the safe return to work. Data used to develop the Physical Work Capacity evaluation comes from 20 years of preemployment research completed at the University of Houston. The purpose of this research was to validate pre-employment tests and define physiologically justified standards or accurate scores. The ergonomic principle is to match the worker to the demands of the job. This validation research is the linkage between test results and job tasks. The Functional Capacity component assesses Work Capacity and physical fitness. The fitness components include maximum aerobic capacity (VO2max), body composition, and flexibility. These are the common components included in adult fitness test batteries (Baumgartner & Jackson, 1999; Golding, Meyers & Sinning, 1989).
PHYSICAL WORK CAPACITY AND FUNCTIONAL CAPACITY EVALUATION SYSTEM, Model 32601PWCFC DETAILS The two components of the PWCFC Evaluation System are Physical Work Capacity (PWC) and Functional Capacity (FC). The Physical Work Capacity component evaluates the capacity of an individual to perform physically demanding work tasks. System input includes the physical ability test results and demographic data. Output is a computergenerated report that assesses the Physical Work Capacity. The report helps employers make either of two employment decisions, which are: Pre-employment: The PWC report evaluates the capacity of a job applicant to perform physically demanding work tasks. Return-to-Work: The FC report evaluates the capacity of an employee to perform physically demanding tasks at a level that allows for the safe return to work. Data used to develop the Physical Work Capacity evaluation comes from 20 years of preemployment research completed at the University of Houston. The purpose of this research was to validate pre-employment tests and define physiologically justified standards or accurate scores. The ergonomic principle is to match the worker to the demands of the job. This validation research is the linkage between test results and job tasks. The Functional Capacity component assesses Work Capacity and physical fitness. The fitness components include maximum aerobic capacity (VO2max), body composition, and flexibility. These are the common components included in adult fitness test batteries (Baumgartner & Jackson, 1999; Golding, Meyers & Sinning, 1989).
PHYSICAL WORK CAPACITY AND FUNCTIONAL CAPACITY EVALUATION SYSTEM, Model 32601PWCFC DETAILS The two components of the PWCFC Evaluation System are Physical Work Capacity (PWC) and Functional Capacity (FC). The Physical Work Capacity component evaluates the capacity of an individual to perform physically demanding work tasks. System input includes the physical ability test results and demographic data. Output is a computergenerated report that assesses the Physical Work Capacity. The report helps employers make either of two employment decisions, which are: Pre-employment: The PWC report evaluates the capacity of a job applicant to perform physically demanding work tasks. Return-to-Work: The FC report evaluates the capacity of an employee to perform physically demanding tasks at a level that allows for the safe return to work. Data used to develop the Physical Work Capacity evaluation comes from 20 years of preemployment research completed at the University of Houston. The purpose of this research was to validate pre-employment tests and define physiologically justified standards or accurate scores. The ergonomic principle is to match the worker to the demands of the job. This validation research is the linkage between test results and job tasks. The Functional Capacity component assesses Work Capacity and physical fitness. The fitness components include maximum aerobic capacity (VO2max), body composition, and flexibility. These are the common components included in adult fitness test batteries (Baumgartner & Jackson, 1999; Golding, Meyers & Sinning, 1989).
PHYSICAL WORK CAPACITY AND FUNCTIONAL CAPACITY EVALUATION SYSTEM, Model 32601PWCFC DETAILS The two components of the PWCFC Evaluation System are Physical Work Capacity (PWC) and Functional Capacity (FC). The Physical Work Capacity component evaluates the capacity of an individual to perform physically demanding work tasks. System input includes the physical ability test results and demographic data. Output is a computergenerated report that assesses the Physical Work Capacity. The report helps employers make either of two employment decisions, which are: Pre-employment: The PWC report evaluates the capacity of a job applicant to perform physically demanding work tasks. Return-to-Work: The FC report evaluates the capacity of an employee to perform physically demanding tasks at a level that allows for the safe return to work. Data used to develop the Physical Work Capacity evaluation comes from 20 years of preemployment research completed at the University of Houston. The purpose of this research was to validate pre-employment tests and define physiologically justified standards or accurate scores. The ergonomic principle is to match the worker to the demands of the job. This validation research is the linkage between test results and job tasks. The Functional Capacity component assesses Work Capacity and physical fitness. The fitness components include maximum aerobic capacity (VO2max), body composition, and flexibility. These are the common components included in adult fitness test batteries (Baumgartner & Jackson, 1999; Golding, Meyers & Sinning, 1989).
PHYSICAL WORK CAPACITY AND FUNCTIONAL CAPACITY EVALUATION SYSTEM, Model 32601PWCFC DETAILS The two components of the PWCFC Evaluation System are Physical Work Capacity (PWC) and Functional Capacity (FC). The Physical Work Capacity component evaluates the capacity of an individual to perform physically demanding work tasks. System input includes the physical ability test results and demographic data. Output is a computergenerated report that assesses the Physical Work Capacity. The report helps employers make either of two employment decisions, which are: Pre-employment: The PWC report evaluates the capacity of a job applicant to perform physically demanding work tasks. Return-to-Work: The FC report evaluates the capacity of an employee to perform physically demanding tasks at a level that allows for the safe return to work. Data used to develop the Physical Work Capacity evaluation comes from 20 years of preemployment research completed at the University of Houston. The purpose of this research was to validate pre-employment tests and define physiologically justified standards or accurate scores. The ergonomic principle is to match the worker to the demands of the job. This validation research is the linkage between test results and job tasks. The Functional Capacity component assesses Work Capacity and physical fitness. The fitness components include maximum aerobic capacity (VO2max), body composition, and flexibility. These are the common components included in adult fitness test batteries (Baumgartner & Jackson, 1999; Golding, Meyers & Sinning, 1989).
PHYSICAL WORK CAPACITY AND FUNCTIONAL CAPACITY EVALUATION SYSTEM, Model 32601PWCFC DETAILS The two components of the PWCFC Evaluation System are Physical Work Capacity (PWC) and Functional Capacity (FC). The Physical Work Capacity component evaluates the capacity of an individual to perform physically demanding work tasks. System input includes the physical ability test results and demographic data. Output is a computergenerated report that assesses the Physical Work Capacity. The report helps employers make either of two employment decisions, which are: Pre-employment: The PWC report evaluates the capacity of a job applicant to perform physically demanding work tasks. Return-to-Work: The FC report evaluates the capacity of an employee to perform physically demanding tasks at a level that allows for the safe return to work. Data used to develop the Physical Work Capacity evaluation comes from 20 years of preemployment research completed at the University of Houston. The purpose of this research was to validate pre-employment tests and define physiologically justified standards or accurate scores. The ergonomic principle is to match the worker to the demands of the job. This validation research is the linkage between test results and job tasks. The Functional Capacity component assesses Work Capacity and physical fitness. The fitness components include maximum aerobic capacity (VO2max), body composition, and flexibility. These are the common components included in adult fitness test batteries (Baumgartner & Jackson, 1999; Golding, Meyers & Sinning, 1989).
PHYSICAL WORK CAPACITY AND FUNCTIONAL CAPACITY EVALUATION SYSTEM, Model 32601PWCFC DETAILS The two components of the PWCFC Evaluation System are Physical Work Capacity (PWC) and Functional Capacity (FC). The Physical Work Capacity component evaluates the capacity of an individual to perform physically demanding work tasks. System input includes the physical ability test results and demographic data. Output is a computergenerated report that assesses the Physical Work Capacity. The report helps employers make either of two employment decisions, which are: Pre-employment: The PWC report evaluates the capacity of a job applicant to perform physically demanding work tasks. Return-to-Work: The FC report evaluates the capacity of an employee to perform physically demanding tasks at a level that allows for the safe return to work. Data used to develop the Physical Work Capacity evaluation comes from 20 years of preemployment research completed at the University of Houston. The purpose of this research was to validate pre-employment tests and define physiologically justified standards or accurate scores. The ergonomic principle is to match the worker to the demands of the job. This validation research is the linkage between test results and job tasks. The Functional Capacity component assesses Work Capacity and physical fitness. The fitness components include maximum aerobic capacity (VO2max), body composition, and flexibility. These are the common components included in adult fitness test batteries (Baumgartner & Jackson, 1999; Golding, Meyers & Sinning, 1989).
PHYSICAL WORK CAPACITY AND FUNCTIONAL CAPACITY EVALUATION SYSTEM, Model 32601PWCFC DETAILS The two components of the PWCFC Evaluation System are Physical Work Capacity (PWC) and Functional Capacity (FC). The Physical Work Capacity component evaluates the capacity of an individual to perform physically demanding work tasks. System input includes the physical ability test results and demographic data. Output is a computergenerated report that assesses the Physical Work Capacity. The report helps employers make either of two employment decisions, which are: Pre-employment: The PWC report evaluates the capacity of a job applicant to perform physically demanding work tasks. Return-to-Work: The FC report evaluates the capacity of an employee to perform physically demanding tasks at a level that allows for the safe return to work. Data used to develop the Physical Work Capacity evaluation comes from 20 years of preemployment research completed at the University of Houston. The purpose of this research was to validate pre-employment tests and define physiologically justified standards or accurate scores. The ergonomic principle is to match the worker to the demands of the job. This validation research is the linkage between test results and job tasks. The Functional Capacity component assesses Work Capacity and physical fitness. The fitness components include maximum aerobic capacity (VO2max), body composition, and flexibility. These are the common components included in adult fitness test batteries (Baumgartner & Jackson, 1999; Golding, Meyers & Sinning, 1989).
相关产品


 显示该栏目以下所有产品
显示该栏目以下所有产品





