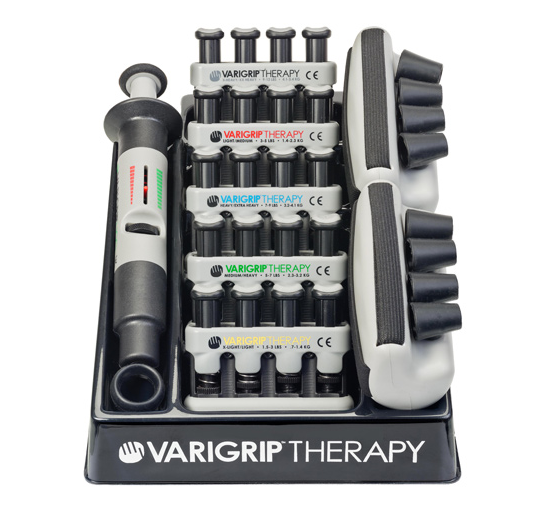
ARAT手臂动作调查测试评估箱-上肢动作研究量表(ARAT)套件
ARAT手臂动作调查测试评估箱-上肢动作研究量表(ARAT)套件
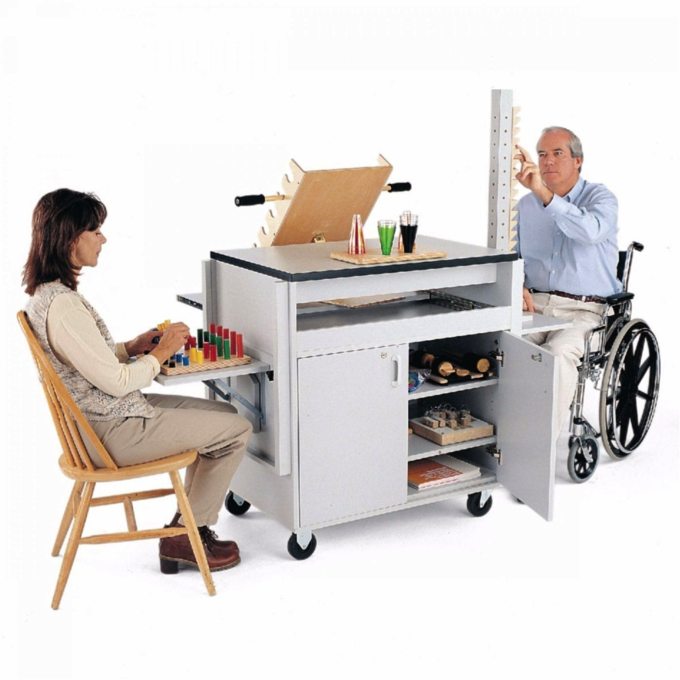
ARAT上肢动作研究量表(Action Research Arm Test),是一个用来评估由于大脑皮层受到持续损伤而导致肢体功能瘫痪的个体上肢功能具体变化的指标(Lyle,1981)。它通过让客户操作不同大小、重量和形状的物体来评价其能力,因此被认为是一种特别测试手臂活动限度的方式(Platz, Pinkowski, Kim, di Bella, & Johnson, 2005)。
经验证,与其他量表相比,上肢动作研究量表(ARAT)在脑卒中患者中具有良好的会聚效度、区分效度和同时效度。
ARAT中的19项评估被分成4个子测试(抓取和放置GRASP,握取和放置GRIP,捏取和放置PINCH,手臂简单粗大运动GROSS MOVEMENT)。每一项目的表现通过以下4个等级进行得分评价:
3分: 测试完成得很完美。
2分: 完成了测试。但明显比未受影响的一侧需要更多的时间和/或有较大的困难。动作表现的慢和笨拙。
1分: 完成部分测试。能够从工作平台上拿起或抬起测试物件,但无法将其放置在正确的位置。比如,在“将水从一个杯子倒到另一个杯子”的测试项中,能够拿起杯子,但无法将水倒进另一个杯子中。在第4项评估大项(简单粗大运动评估)中,能够抬起手臂,得分为1。
0分: 不能完成测试任务的任何部分。
-
如果子测试的第1项(最难的项目)得分为3分,患者将获得该子测试所有项目的满分。然后转到下一个子测试继续测试。
-
如果子测试第一项得分低于3分,则使用该子测试第二项(每个子测试中最简单的一项)。
-
如果子测试第二项得分为0分,则该子测试总得分为0分,应该转到下一个子测试继续测试。
如何使用请收看,ARAT手臂动作调查测试评估箱-上肢动作研究量表(ARAT)套件使用视频演示
ARAT手臂动作调查测试评估箱(Action Research Arm Test)文献索引(部分):
-
Stroke. 2022 Feb;53(2):578-585.doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.121.035170. Epub 2021 Oct 4.
《Fast Outcome Categorization of the Upper Limb After Stroke》
-
IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2022 Feb;69(2):945-954.doi: 10.1109/TBME.2021.3110432. Epub 2022 Jan 20.
《Poststroke Grasp Ability Assessment Using an Intelligent Data Glove Based on Action Research Arm Test: Development, Algorithms, and Experiments》
-
Front Neurol. 2022 Feb 17;13:804133.doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.804133. eCollection 2022.
《Clinical Imaging-Derived Metrics of Corticospinal Tract Structural Integrity Are Associated With Post-stroke Motor Outcomes: A Retrospective Study》
-
Games Health J. 2022 Jan 31.doi: 10.1089/g4h.2021.0197. Online ahead of print.
《The Effect of Robot-Mediated Virtual Reality Gaming on Upper Limb Spasticity Poststroke: A Randomized-Controlled Trial》
-
J Rehabil Med. 2022 Mar 10.doi: 10.2340/jrm.v54.29. Online ahead of print.
Visually induced kinaesthetic illusion combined with therapeutic exercise for patients with chronic stroke: a pilot study
-
Neural Plast. 2022 Jan 24;2022:7399995.doi: 10.1155/2022/7399995. eCollection 2022.
《The Effect of Virtual Reality on Motor Anticipation and Hand Function in Patients with Subacute Stroke: A Randomized Trial on Movement-Related Potential》
-
Physiother Res Int. 2022 Jan 17;e1937.doi: 10.1002/pri.1937. Online ahead of print.
《Predicting post-stroke motor recovery of upper extremity using clinical variables and performance assays: A prospective cohort study protocol》
-
Med Biol Eng Comput. 2022 Jan;60(1):249-261.doi: 10.1007/s11517-021-02467-y. Epub 2021 Nov 25.
《Personalized prediction of rehabilitation outcomes in multiple sclerosis: a proof-of-concept using clinical data, digital health metrics, and machine learning》
-
Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2022 Jan 15;62(1):35-44.doi: 10.2176/nmc.oa.2020-0408. Epub 2021 Nov 3.
《Effect of Robot-assisted Rehabilitation to Botulinum Toxin A Injection for Upper Limb Disability in Patients with Chronic Stroke: A Case Series and Systematic Review》
-
Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2022 Feb;46:101520.doi: 10.1016/j.ctcp.2021.101520. Epub 2021 Dec 2.
《Effects of dry needling plus exercise therapy on post-stroke spasticity and motor function: A case report》
-
BMJ Open. 2022 Jan 13;12(1):e053991.doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-053991.
《Corticocortical paired associative stimulation for treating motor dysfunction after stroke: study protocol for a randomised sham-controlled double-blind clinical trial》
-
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Sep 28;118(39):e2026676118.doi: 10.1073/pnas.2026676118.
《Critical Period After Stroke Study (CPASS): A phase II clinical trial testing an optimal time for motor recovery after stroke in humans》
-
J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2021 Sep 26;18(1):147.doi: 10.1186/s12984-021-00938-9.
《Associations between upper extremity functioning and kinematics in people with spinal cord injury》
-
Disabil Rehabil. 2021 Sep 19;1-9.doi: 10.1080/09638288.2021.1973121. Online ahead of print.
《Home mirror therapy: a randomized controlled pilot study comparing unimanual and bimanual mirror therapy for improved arm and hand function post-stroke.》
-
J Neural Eng. 2021 May 14;18(4).doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/abfc1e.
《Prognosis of stroke upper limb recovery with physiological variables using regression tree ensembles》
-
J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2021 May 31;18(1):91.doi: 10.1186/s12984-021-00885-5.
《Augmented efficacy of intermittent theta burst stimulation on the virtual reality-based cycling training for upper limb function in patients with stroke: a double-blinded, randomized controlled trial》
-
Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2021 May;35(5):393-405.doi: 10.1177/15459683211000730. Epub 2021 Mar 20.
《Comparing a Novel Neuroanimation Experience to Conventional Therapy for High-Dose Intensive Upper-Limb Training in Subacute Stroke: The SMARTS2 Randomized Trial》
-
Front Neurosci. 2021 Sep 27;15:670953.doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.670953. eCollection 2021.
《Brain-Computer Interface Training With Functional Electrical Stimulation: Facilitating Changes in Interhemispheric Functional Connectivity and Motor Outcomes Post-stroke》
-
JMIR Serious Games. 2021 Nov 23;9(4):e30184.doi: 10.2196/30184.
《Long-term Effectiveness and Adoption of a Cellphone Augmented Reality System on Patients with Stroke: Randomized Controlled Trial》
-
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Nov 3;2021:1116126.doi: 10.1155/2021/1116126. eCollection 2021.
《Motor Imagery-Based Brain-Computer Interface Combined with Multimodal Feedback to Promote Upper Limb Motor Function after Stroke: A Preliminary Study》
-
Front Aging Neurosci. 2021 Nov 2;13:731343.doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.731343. eCollection 2021.
《The Effect of Virtual Reality-Based Therapy on Improving Upper Limb Functions in Individuals With Stroke: A Randomized Control Trial》
-
J Healthc Eng. 2021 Aug 19;2021:4071645.doi: 10.1155/2021/4071645. eCollection 2021.
《Kinematic Evaluation via Inertial Measurement Unit Associated with Upper Extremity Motor Function in Subacute Stroke: A Cross-Sectional Study》
-
Front Hum Neurosci. 2021 Jun 7;15:656975.doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2021.656975. eCollection 2021.
《Brain-Computer Interface Coupled to a Robotic Hand Orthosis for Stroke Patients' Neurorehabilitation: A Crossover Feasibility Study》
-
PLoS One. 2021 Dec 9;16(12):e0260743.doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0260743. eCollection 2021.
《Changes in motor paralysis involving upper extremities of outpatient chronic stroke patients from temporary rehabilitation interruption due to spread of COVID-19 infection: An observational study on pre- and post-survey data without a control group》
-
J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2021 Sep 19;18(1):141.doi: 10.1186/s12984-021-00934-z.
《HoMEcare aRm rehabiLItatioN (MERLIN): preliminary evidence of long term effects of telerehabilitation using an unactuated training device on upper limb function after stroke》
-
Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2021 Sep;35(9):836-848.doi: 10.1177/15459683211032967. Epub 2021 Jul 19.
《A Self-Empowered Upper Limb Repetitive Engagement Program to Improve Upper Limb Recovery Early Post-Stroke: Phase II Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial》
-
Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2021 Nov;102(11):2074-2082.doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2021.06.001. Epub 2021 Jun 24.
《Exoskeleton-Assisted Anthropomorphic Movement Training (EAMT) for Poststroke Upper Limb Rehabilitation: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial》
-
J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2021 Aug;30(8):105889.doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2021.105889. Epub 2021 May 29.
《Relationship Between Motor Function, DTI, and Neurophysiological Parameters in Patients with Stroke in the Recovery Rehabilitation unit》
-
Mult Scler Int. 2021 Jun 26;2021:5588335.doi: 10.1155/2021/5588335. eCollection 2021.
《A Descriptive Correlational Study to Evaluate Three Measures of Assessing Upper Extremity Function in Individuals with Multiple Sclerosis》
-
Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021 Apr 12;9:660015.doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.660015. eCollection 2021.
《Association Between Finger-to-Nose Kinematics and Upper Extremity Motor Function in Subacute Stroke: A Principal Component Analysis 》
-
Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2021 Apr;35(4):334-345.doi: 10.1177/1545968321997769. Epub 2021 Mar 3.
《A Robotic System with EMG-Triggered Functional Eletrical Stimulation for Restoring Arm Functions in Stroke Survivors》
-
J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2021 Jul;30(7):105812.doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2021.105812. Epub 2021 Apr 22.
《Effects of a Soft Robotic Hand for Hand Rehabilitation in Chronic Stroke Survivors》
-
J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2021 Sep 15;18(1):137.doi: 10.1186/s12984-021-00930-3.
《Home-based self-help telerehabilitation of the upper limb assisted by an electromyography-driven wrist/hand exoneuromusculoskeleton after stroke》
-
Behav Neurol. 2021 Nov 9;2021:9417173.doi: 10.1155/2021/9417173. eCollection 2021.
《Associations between Upper Extremity Motor Function and Aphasia after Stroke: A Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study》
-
Neural Plast. 2021 Dec 22;2021:1987662.doi: 10.1155/2021/1987662. eCollection 2021.
《Effectiveness of Contralaterally Controlled Functional Electrical Stimulation versus Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation on Upper Limb Motor Functional Recovery in Subacute Stroke Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial》
-
Top Stroke Rehabil. 2020 Mar;27(2):127-136.
《Clinimetric properties of the action research arm test for the assessment of arm activity in hemiparetic patients after stroke》
-
Rev Med Chil. 2012 Jan;140(1):59-65.
《Validation of "Action Research Arm Test" (ARAT) in Chilean patients with a paretic upper limb after a stroke》
-
J Phys Ther Sci. 2018 Oct;30(10):1271-1277.
《Test-retest reliability of physiotherapists using the action research arm test in chronic stroke》
-
Biomed Res Int. 2019 Oct 7;2019:8270187.
《Responsiveness and Predictive Ability of the Chinese Version of the Action Research Arm Test in People with Cerebral Infarction》
-
Aust Occup Ther J. 2018 Oct;65(5):449-471.
《A systematic review of the psychometric properties of the Action Research Arm Test in neurorehabilitation》
-
Front Neurol. 2019 May 29;10:540.
《Inter-rater and Intra-rater Reliability of the Chinese Version of the Action Research Arm Test in People With Stroke》
-
J Med Assoc Thai . 2012 Apr;95(4):590-7.
《Correlation between the action research arm test and the box and block test of upper extremity function in stroke patients》
-
Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2012 Jun;93(6):1039-45.
《Rasch validation and predictive validity of the action research arm test in patients receiving stroke rehabilitation》
-
J Rehabil Med. 2006 Nov;38(6):375-80.
《Validation of the action research arm test using item response theory in patients after stroke》
-
Neurorehabil Neural Repair. Jan-Feb 2008;22(1):78-90.
《A standardized approach to performing the action research arm test》
-
Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2006 Dec;87(12):1605-10.
《Measurement of upper-extremity function early after stroke: properties of the action research arm test》
-
J Rehabil Med. 2014 Sep;46(8):738-45.
《Intra-rater and inter-rater reliability at the item level of the Action Research Arm Test for patients with stroke》
-
Age Ageing. 1998 Mar;27(2):107-13.
《Inter-rater reliability and validity of the action research arm test in stroke patients》
|
ARAT |
上肢动作研究量表(ARAT)套件 |
电邮询价 |
ARAT手臂动作调查测试评估箱-上肢动作研究量表(ARAT)套件使用视频演示
Action Research Arm Test (ARAT) Kit The Action Research Arm Test (ARAT) is an evaluative measure to assess specific changes in limb function among individuals who sustained cortical damage resulting in hemiplegia (Lyle, 1981). It assesses a client’s ability to handle objects differing in size, weight and shape and therefore can be considered to be an arm-specific measure of activity limitation (Platz, Pinkowski, Kim, di Bella, & Johnson, 2005). The ARATs is a 19 item measure divided into 4 sub-tests (grasp, grip, pinch, and gross arm movement). Performance on each item is rated on a 4-point ordinal scale ranging from: 3: Performs test normally 2: Completes test, but takes abnormally long or has great difficulty 1: Performs test partially 0: Can perform no part of test ARAT Action Research Arm Test (ARAT) Kit Email for Quotation
Action Research Arm Test (ARAT) Kit The Action Research Arm Test (ARAT) is an evaluative measure to assess specific changes in limb function among individuals who sustained cortical damage resulting in hemiplegia (Lyle, 1981). It assesses a client’s ability to handle objects differing in size, weight and shape and therefore can be considered to be an arm-specific measure of activity limitation (Platz, Pinkowski, Kim, di Bella, & Johnson, 2005). The ARATs is a 19 item measure divided into 4 sub-tests (grasp, grip, pinch, and gross arm movement). Performance on each item is rated on a 4-point ordinal scale ranging from: 3: Performs test normally 2: Completes test, but takes abnormally long or has great difficulty 1: Performs test partially 0: Can perform no part of test ARAT Action Research Arm Test (ARAT) Kit Email for Quotation
Action Research Arm Test (ARAT) Kit The Action Research Arm Test (ARAT) is an evaluative measure to assess specific changes in limb function among individuals who sustained cortical damage resulting in hemiplegia (Lyle, 1981). It assesses a client’s ability to handle objects differing in size, weight and shape and therefore can be considered to be an arm-specific measure of activity limitation (Platz, Pinkowski, Kim, di Bella, & Johnson, 2005). The ARATs is a 19 item measure divided into 4 sub-tests (grasp, grip, pinch, and gross arm movement). Performance on each item is rated on a 4-point ordinal scale ranging from: 3: Performs test normally 2: Completes test, but takes abnormally long or has great difficulty 1: Performs test partially 0: Can perform no part of test ARAT Action Research Arm Test (ARAT) Kit Email for Quotation
Action Research Arm Test (ARAT) Kit The Action Research Arm Test (ARAT) is an evaluative measure to assess specific changes in limb function among individuals who sustained cortical damage resulting in hemiplegia (Lyle, 1981). It assesses a client’s ability to handle objects differing in size, weight and shape and therefore can be considered to be an arm-specific measure of activity limitation (Platz, Pinkowski, Kim, di Bella, & Johnson, 2005). The ARATs is a 19 item measure divided into 4 sub-tests (grasp, grip, pinch, and gross arm movement). Performance on each item is rated on a 4-point ordinal scale ranging from: 3: Performs test normally 2: Completes test, but takes abnormally long or has great difficulty 1: Performs test partially 0: Can perform no part of test ARAT Action Research Arm Test (ARAT) Kit Email for Quotation
Action Research Arm Test (ARAT) Kit The Action Research Arm Test (ARAT) is an evaluative measure to assess specific changes in limb function among individuals who sustained cortical damage resulting in hemiplegia (Lyle, 1981). It assesses a client’s ability to handle objects differing in size, weight and shape and therefore can be considered to be an arm-specific measure of activity limitation (Platz, Pinkowski, Kim, di Bella, & Johnson, 2005). The ARATs is a 19 item measure divided into 4 sub-tests (grasp, grip, pinch, and gross arm movement). Performance on each item is rated on a 4-point ordinal scale ranging from: 3: Performs test normally 2: Completes test, but takes abnormally long or has great difficulty 1: Performs test partially 0: Can perform no part of test ARAT Action Research Arm Test (ARAT) Kit Email for Quotation
Action Research Arm Test (ARAT) Kit The Action Research Arm Test (ARAT) is an evaluative measure to assess specific changes in limb function among individuals who sustained cortical damage resulting in hemiplegia (Lyle, 1981). It assesses a client’s ability to handle objects differing in size, weight and shape and therefore can be considered to be an arm-specific measure of activity limitation (Platz, Pinkowski, Kim, di Bella, & Johnson, 2005). The ARATs is a 19 item measure divided into 4 sub-tests (grasp, grip, pinch, and gross arm movement). Performance on each item is rated on a 4-point ordinal scale ranging from: 3: Performs test normally 2: Completes test, but takes abnormally long or has great difficulty 1: Performs test partially 0: Can perform no part of test ARAT Action Research Arm Test (ARAT) Kit Email for Quotation
Action Research Arm Test (ARAT) Kit The Action Research Arm Test (ARAT) is an evaluative measure to assess specific changes in limb function among individuals who sustained cortical damage resulting in hemiplegia (Lyle, 1981). It assesses a client’s ability to handle objects differing in size, weight and shape and therefore can be considered to be an arm-specific measure of activity limitation (Platz, Pinkowski, Kim, di Bella, & Johnson, 2005). The ARATs is a 19 item measure divided into 4 sub-tests (grasp, grip, pinch, and gross arm movement). Performance on each item is rated on a 4-point ordinal scale ranging from: 3: Performs test normally 2: Completes test, but takes abnormally long or has great difficulty 1: Performs test partially 0: Can perform no part of test ARAT Action Research Arm Test (ARAT) Kit Email for Quotation
Action Research Arm Test (ARAT) Kit The Action Research Arm Test (ARAT) is an evaluative measure to assess specific changes in limb function among individuals who sustained cortical damage resulting in hemiplegia (Lyle, 1981). It assesses a client’s ability to handle objects differing in size, weight and shape and therefore can be considered to be an arm-specific measure of activity limitation (Platz, Pinkowski, Kim, di Bella, & Johnson, 2005). The ARATs is a 19 item measure divided into 4 sub-tests (grasp, grip, pinch, and gross arm movement). Performance on each item is rated on a 4-point ordinal scale ranging from: 3: Performs test normally 2: Completes test, but takes abnormally long or has great difficulty 1: Performs test partially 0: Can perform no part of test ARAT Action Research Arm Test (ARAT) Kit Email for Quotation
Action Research Arm Test (ARAT) Kit The Action Research Arm Test (ARAT) is an evaluative measure to assess specific changes in limb function among individuals who sustained cortical damage resulting in hemiplegia (Lyle, 1981). It assesses a client’s ability to handle objects differing in size, weight and shape and therefore can be considered to be an arm-specific measure of activity limitation (Platz, Pinkowski, Kim, di Bella, & Johnson, 2005). The ARATs is a 19 item measure divided into 4 sub-tests (grasp, grip, pinch, and gross arm movement). Performance on each item is rated on a 4-point ordinal scale ranging from: 3: Performs test normally 2: Completes test, but takes abnormally long or has great difficulty 1: Performs test partially 0: Can perform no part of test ARAT Action Research Arm Test (ARAT) Kit Email for Quotation



 显示该栏目以下所有产品
显示该栏目以下所有产品